Create Your Own SSH UDP CUSTOM Server Account
Secure and Easy Tunneling with Free Premium UDP Custom Account – Active for 7 or 5 Days
SSH UDP CUSTOM Server in USA
Please don’t use Torrent, DDoS, Spamming and any illegal activity with our server!
UDP Server Creation
How to Use this UDP server
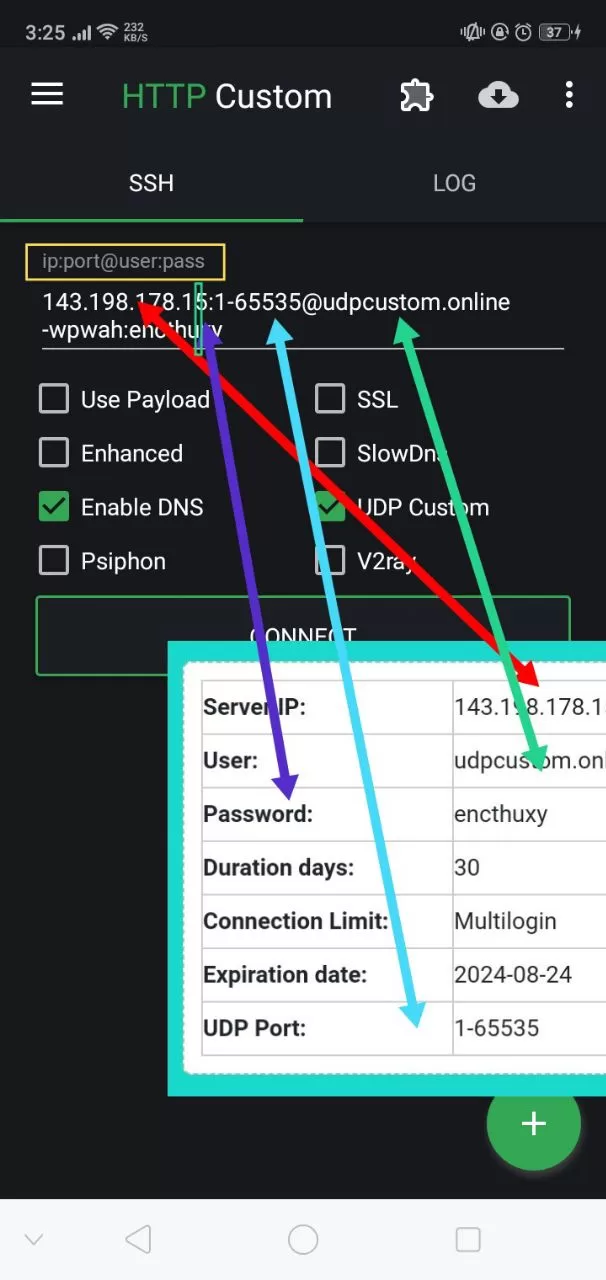
How to Use HTTP Custom
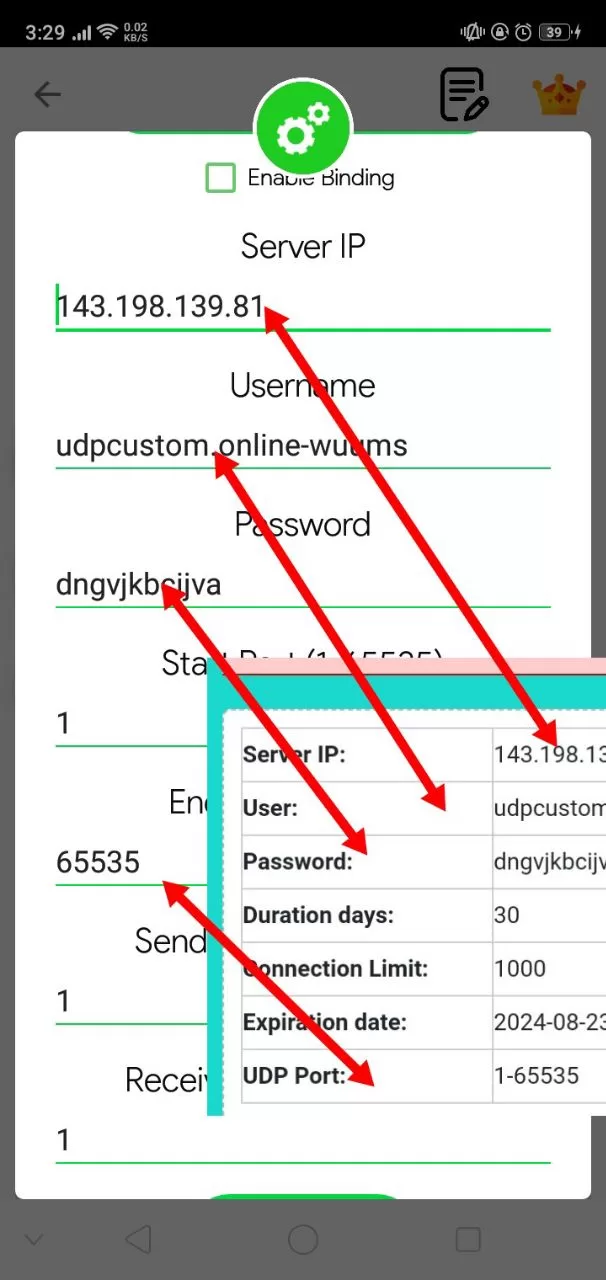
How to Use Socks IP
User Datagram Protocol (UDP): An Overview
The User Datagram Protocol, commonly known as UDP, is one of the core members of the Internet Protocol Suite. It serves as a crucial component in the world of network communications, offering a streamlined approach to data transfer. This article will delve into the fundamentals of UDP, its characteristics, use cases, and how it compares to its counterpart, TCP.
What is UDP?
UDP is a connectionless transport layer protocol that facilitates fast, efficient data transmission over IP networks. Unlike its more reliable cousin TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), UDP prioritizes speed over reliability, making it an ideal choice for certain types of network applications.
Key Characteristics of UDP
- Connectionless: UDP doesn’t establish a connection before sending data. It simply fires off packets to the destination without any handshaking process.
- Unreliable: There’s no guarantee that UDP packets will reach their destination. They may arrive out of order, appear duplicated, or not arrive at all.
- Low overhead: Due to its simplicity, UDP has minimal protocol overhead, resulting in faster data transmission.
- No congestion control: UDP doesn’t adjust its transmission rate based on network congestion.
- Stateless: Each UDP packet is handled independently of other packets.
UDP Packet Structure
A UDP packet, also known as a datagram, consists of a header and a data section. The header is 8 bytes long and contains four fields:
- Source Port (16 bits)
- Destination Port (16 bits)
- Length (16 bits)
- Checksum (16 bits)
The data section follows the header and contains the actual payload.
Use Cases for UDP
UDP is particularly useful in scenarios where speed is more critical than reliability:
- Real-time applications: Video streaming, VoIP, online gaming
- DNS (Domain Name System): For quick domain name resolutions
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol): For network device management
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): For dynamic IP address allocation
UDP vs. TCP
While both UDP and TCP are transport layer protocols, they serve different purposes:
| Feature | UDP | TCP |
|---|---|---|
| Connection | Connectionless | Connection-oriented |
| Reliability | Unreliable | Reliable |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Ordering | No packet ordering | Maintains packet order |
| Error checking | Basic (checksum only) | Extensive |
| Flow control | No | Yes |
| Use cases | Real-time apps, simple queries | Web browsing, email, file transfer |
Advantages and Disadvantages of UDP
Advantages:
- Faster data transmission
- Lower latency
- Simpler implementation
- Suitable for real-time applications
Disadvantages:
- No guarantee of delivery
- No packet ordering
- Vulnerable to packet loss
- Limited error checking
Conclusion
UDP plays a vital role in modern network communications, offering a lightweight, speedy alternative to TCP. While its lack of reliability makes it unsuitable for certain applications, its efficiency and low latency make it indispensable for real-time data transmission and quick, simple network operations. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of UDP is crucial for network administrators, developers, and anyone involved in designing or managing network applications.
